Strategies to support crystallization for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells

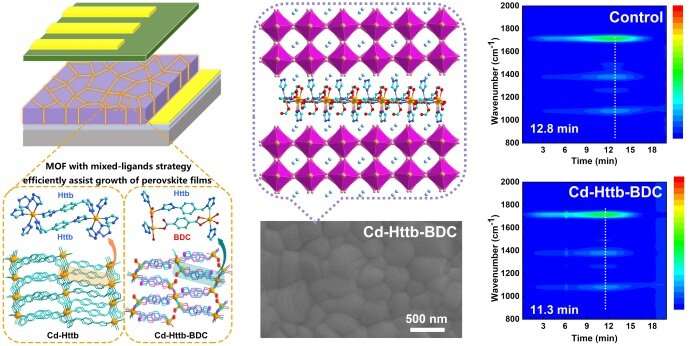
A novel MOF (Cd-Httb-BDC) engineered through a mixed ligand strategy was used as a heterogeneous nucleation center to simultaneously passivate deep-level defects and aid in the process. crystallization of high-quality perovskite films with enlarged grain sizes towards efficient growth and stable PSCs. Credit: Energy Chemistry Magazine
Recent developments have allowed perovskite solar cells (PSCs) to achieve energy conversion efficiency in excess of 25.7%; therefore, these devices are considered as rising stars in the field of photovoltaics. However, the uniform crystallization of perovskite can lead to disordered crystal orientation and defects in the bulk phase and grain boundaries, thereby limiting PSC performance and stability. Passive regulation and defect crystallization are considered as effective strategies to improve the performance of these devices.
Metal-organic framework (MOF) materials play an important role in tuning perovskite crystallization and passivation disabilities and improve carrier mobility thanks to its high porosity structure, strong functional structural design and other advantages. However, the present study indicates that most MOFs applied to PSCs lack a functional design for their structure. In this case, a mixed ligand strategy can not only design functional MOFs with novel structures, but can also passivate defects and modulate perovskite crystallization through the synergistic effect of selected ligands.
Assistant researchers Yayu Dong, professors Yulin Yang and Ruiqing Fan, associate professor Jian Zhang, and others of Harbin Institute of Technology recently published a manuscript, titled “Metal framework- organic with a mixed coordination strategy as the heterogeneous nucleation center to support efficient crystallization and stable Perovskite Solar Cells,” in Energy Chemistry Magazine.
The flexible organic ligand 5-(4-(1H-1,2,4-triazole-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-tetrazole (Httb) was selected to generate a new 3D MOF (Cd-Httb). The second ligand, 1,4-dicarboxybenzene (H2BDC), then introduced with this MOF to successfully construct another new 3D MOF (Cd-Httb-BDC).
Compared with the control and Cd-Httb, the engineered Cd-Httb-BDC with mixed ligands acts as the nanostructured heterogeneous nucleation and effectively supports the crystallization of perovskite films. High quality large seeds. It also reduces the density of error states, thereby improving the efficiency and stability of the PSC.
This work provides a theoretical basis for the synthesis of novel functional MOFs for PSC preparation, which has great implications for the commercialization of perovskite-based photovoltaic devices.
Yayu Dong et al, Metal-organic framework with mixed ligand strategy as heterogeneous nucleation center to support crystallization for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells, Energy Chemistry Magazine (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2022.10.029
Provided by
Chinese Academy of Sciences
quote: Crystallization support strategy for efficient and stable perovskite solar cells (2022, 29 Nov) retrieved 30 Nov 2022 from https://techxplore.com/news/2022-11-strategy -crystallization-efficiency-stable-perovskite.html
This document is the subject for the collection of authors. Other than any fair dealing for private learning or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content provided is for informational purposes only.




