Researchers develop adaptive directional charging for efficient wireless rechargeable sensor networks

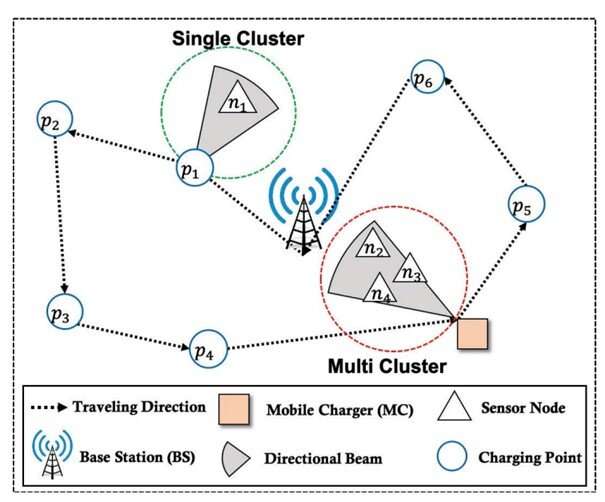
In a new study, researchers from Chung-Ang University have proposed a new energy-saving adaptive directional charging (EEEADC) algorithm that considers the density of sensor nodes to select a sensor module. adaptively charge single or multi-charger in wireless charging sensor network. Credit: Sungrae Cho of Chung-Ang University
Smart factories, vehicles, and cities increasingly use wireless rechargeable sensor networks (WRSNs) for communication. A distinct advantage of WRSNs is that they can be located in remote, inaccessible or even biologically or chemically contaminated areas for communication, surveillance and reconnaissance in military applications. and environment. However, the potential of these WRSNs is limited as they depend on limited power sources such as batteries, which can interfere with their smooth operation.
The main challenge of WRSN is to efficiently charge and maintain the batteries of the sensors in the network. The charging efficiency decreases sharply as the charging distance increases. Therefore, charging once is more energy efficient than charging multiple times because it can charge a sensor node at a closer range. However, when there are multiple buttons, charging multiple times can achieve greater efficiency.
This prompted a team of researchers led by Professor Sungrae Cho, from the School of Computer Science and Engineering, Chung-Ang University, to optimize charging of mobile sensors efficiently through through wireless power transmission technology. As Professor Cho said, “Wireless power transmission using portable chargers is designed to be an efficient method, but without the use of directional antennas, this method will not work.” . So I started researching to see if there’s an effective method? How to use it.”
In a recent article published on IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, researchers have developed an energy-saving adaptive directional charging (EEEADC) algorithm that considers the density of sensor nodes to select single or multiple charges adaptively. Since the EEADC automatically determines the charging strategy based on the charging efficiency, the researchers achieved a charging efficiency equal to or better than that of a single charge and at the same time reduced energy waste due to repeated overuse. charging.
EEADC uses a mean-shift algorithm that considers node density to identify single charge/multi-charge clusters more efficiently than the standard K-Means algorithm used in most Monte Carlo (MC) clustering methods. ). Each cluster is classified as a single or multi-charged cluster depending on the number of sensor nodes it contains. The charging strategy, including charging point, beam direction, charging capacity and charging time, is then determined according to cluster type.
For the multi-charge cluster, the problem of non-convex optimization with many possible regions has led the researchers to use the discrete charging strategy decision algorithm (DCSD) to solve the problem efficiently. DCSD divides the problem into two subproblems. The candidate charge points are obtained by solving the first subproblem. Then, DCSD selects the point with the lowest power consumption among the candidate charging points as the optimal charging point.
The researchers used simulations to compare the EEADC with conventional charging methods in the real world. The team demonstrated that EEADC outperformed existing methods in terms of power consumption and charging latency by 10% and 9%, respectively.
In summary, the adaptive and directional features of the EEADC greatly enhance the energy efficiency of the charging sensors in the WRSN. As Professor Cho explains: “Using this algorithm, charging efficiency can be significantly increased by using a directional antenna and a directional beam to charge the sensor node and the sensors located in close proximity to each other. can be efficiently charged simultaneously.”
Industrial zones such as smart factories, large ships and building site will benefit greatly when this algorithm to recruit. Efficient and effective monitoring of various sites through wireless sensor networks can be achieved seamlessly through this technology. Charging an energy-efficient portable sensor can significantly reduce WRSN maintenance costs.
Donghyun Lee et al., Energy-saving Oriented Charging Strategy for Wireless Rechargeable Sensor Network, IEEE Internet of Things Magazine (2022). DOI: 10.1109/JIOT.2022.3163400
Provided by Chung Ang University
Quote: Researchers developing adaptive directional charging for efficient wireless rechargeable sensor networks (2022, November 15) retrieved November 16, 2022 from https://techxplore .com/news/2022-11-efficiency-wireless-rechargeable-sensor-networks.html
This document is the subject for the collection of authors. Other than any fair dealing for private learning or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content provided is for informational purposes only.




