Composite population and improved social simulation to guide decision-making

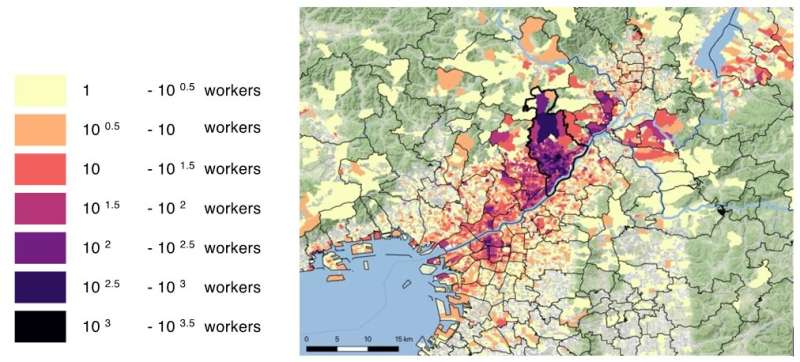
This image shows the possible workplace of simulated workers living in Takatsuki, Japan. With additional information, their movements can be simulated to predict the spread of infectious diseases in the workplace. Credit: Takuya Harada from Shibaura Institute of Technology
Synthetic populations are computer-generated groups of people designed to look like real populations. They are built using publicly available census information about people’s characteristics, such as their age, gender, and job, along with statistical algorithms that help put it all together. together.
Their main application is to conduct so-called social simulations to evaluate different possible solutions to Social Issues, such as transportation, health and housing issues. For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists in many parts of the world conducted social simulations to estimate the number of cases in each country.
In Japan, researchers have performed such simulations using supercomputers under the COVID-19 Simulation & Artificial Intelligence Project led by the Cabinet Secretariat of the Japanese government. from 2020. They have been given considerable consideration when deciding on various political measures, such as PCR testing policies, immigration limits, domestic travel support, vaccination programs, etc.
These simulations are made possible thanks to a composite population that has been prepared and updated under the Joint Research/Use Center for Interdisciplinary Large-scale Information Infrastructure (JHPCN) project. since 2017.
However, this composite Japanese population has one significant limitation—although home address is one of the attributes assigned to each individual, their place of work is not. As a result, this composite population is more accurate at showing the distribution of people at night, but not their daytime distribution or the relationship between the two.
To tackle this problem, a trio of Japanese researchers including Assistant Professor Takuya Harada of the Shibaura Institute of Technology, as well as Dr. Tadahiko Murata and Mr. Daiki Iwase of the Department of Informatics at Kansai University, recently come up with a method to assign work places. attributes for each worker in the aggregate population. Their research was published in IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems.
The main challenge that researchers had to overcome was the lack of statistical information linking people’s home and work locations. In Japan, only local governments whose areas have more than 200,000 residents publish complete destination-destination-industry (ODI) statistics, providing detailed information on the movement of people. workers as well as their industry type (such as retail, construction or manufacturing).
For cities, towns or villages with fewer than 200,000 inhabitants, the available ODI data are less specific and only indicate whether the person works in the same city, in another city within the same province, or in another city. in another city in another province. Unfortunately, about 48% of workers in Japan reside in cities with fewer than 200,000 residents.
Therefore, the team combined the available ODI data with origin-destination (OD) data and developed an innovative workplace assignment method that works for all cities, towns and cities. village in Japan. To check if their method was properly designed, they used it to assign workplaces to people in cities with more than 200,000 residents and compared the results with data. Complete ODI is available.
For the city of Takatsuki in Osaka prefecture that the researchers used as an example in their paper, the proposed method was able to designate the right city as the workplace for 88.2% of the workers.
The possible application For detailed social simulations using synthetic populations there are many ways, as Professor Murata of Kansai University commented: “Real-scale social simulations can be used to estimate the effects of urban development, including housing and transportation projects, as well as the effects of social programs implemented by national or local governments, they can also be used for rescue and relief programs in the face of disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, floods, hurricanes and pandemics.”
Simply put, social simulations can help decision makers accurately visualize possible futures.
Another important aspect of synthetic populations is that they do not have data privacy concerns. “Aggregate populations are a secure technology because no personal information is used,” explains Assistant Professor Harada, “Because we aggregate multiple sets of populations with similar characteristics. statistics, third parties cannot determine whether real information was included.”
This study marks the world’s first aggregated population for which workplace information is publicly available to engineers and researchers. They can be requested at the first author’s website.
The team is working on using their new workplace assignment method to estimate the time of day population distributed throughout Japan. It is very likely that further progress in synthetic populations will lead to better decision making in the near future.
More information:
Tadahiko Murata et al., Workplace assignment for workers in the general community in Japan, IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems (2022). DOI: 10.1109/TCSS.2022.3217614
First author’s website: www.res.kutc.kansai-u.ac.jp/~m … istribution/?lang=en
Provided by Shibaura Institute of Technology
quote: Population aggregation and improved social simulations to guide decision-making (2023, January 19) retrieved January 19, 2023 from https://techxplore.com/news/2023- 01-synthetic-populations-social-simulations-decision-making.html
This document is the subject for the collection of authors. Other than any fair dealing for private learning or research purposes, no part may be reproduced without written permission. The content provided is for informational purposes only.




